 Guide to Harmonic Trading and Harmonic Patterns
Guide to Harmonic Trading and Harmonic Patterns
Harmonic Trading is a highly advanced technical analysis method that seeks to forecast major price reversals by recognizing specific chart patterns and aligning them with precise Fibonacci ratios.
These are the basic Harmonic Ratios:
I. Primary Ratios
• 0.618 = Primary Ratio | 1.618 = Primary Projection
II. Derived Ratios
• 0.786 | 0.886 | 1.13 | 1.27
III. Complementary Ratios
• 0.382 | 0.50 | 0.707 | 1.41 | 2.0 | 2.24 | 2.618 | 3.14 | 3.618
Based on the above ratios we can distinguish 6 basic harmonic patterns.
(1) ABCD Pattern
(2) Three-Drive Pattern
(3) Gartley 222
(4) Harmonic Bat
(5) Harmonic Crab
(6) Butterfly Pattern
Core Principles of Harmonic Trading
Harmonic trading is built on the belief that price movements follow natural, repeating geometric patterns governed by Fibonacci ratios. These patterns offer traders a precise framework for identifying high-probability reversal points.
1. Price and Time Symmetry
Markets exhibit geometric behavior shaped by consistent proportional relationships—most notably those derived from Fibonacci ratios. These patterns repeat over time as a reflection of collective human behavior and market psychology.
2. Precision through Fibonacci Ratios
Unlike conventional chart patterns, harmonic patterns demand strict alignment between price swings based on specific Fibonacci retracements and extensions. For example, in many patterns, leg B must retrace exactly 61.8% of leg A. This mathematical structure reduces interpretation bias and increases consistency in pattern identification.
3. Reversal-Oriented Approach
Harmonic patterns are designed to anticipate market turning points rather than trend continuation. Each pattern culminates in a Potential Reversal Zone (PRZ)—a critical area where multiple Fibonacci projections converge. The PRZ serves as a high-probability zone for identifying trend exhaustion and potential reversals.
This is an analysis of all six basic Harmonic Patterns:
(1) The Basic AB=CD Pattern
The AB=CD pattern is a significant four-point harmonic formation and is regarded as the foundational structure for all other harmonic patterns. The AB=CD pattern can be either bullish or bearish.
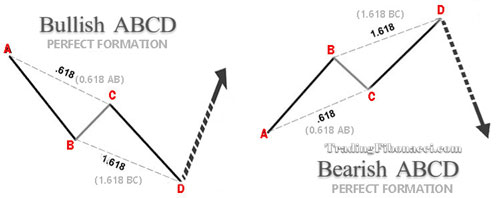 •AB and CD form the legs
•AB and CD form the legs
•BC is the retracement
If AB line equals the CD line, then the point C is indicating the existence of a potential AB=CD pattern, and point D is very crucial as concerns the completion or not of this pattern.
How to identify the Perfect ABCD Formation
(1) Find the Fibonacci retracement tool which is available in almost all modern trading platforms
(2) By applying the Fibonacci retracement tool on AB, the BC retracement must reach the 0.618 level
(2) By applying again the Fibonacci retracement tool on BC, the CD should ideally reach the 1.618 level
The AB=CD Pattern Key Characteristics
1. AB leg must be equivalent to the CD leg near completion
2. The Point C retracement can vary between 0.382 to 0.886 and that creates alternative AB=CD formations
3. The ideal Point C retracement is 0.618 (as seen in the above chart)
4. The BC projection can vary from 1.13 to 2.618 (according to point C retracement)
5. The ideal BC projection is 1.618 (as seen in the above chart)
(2) Three-Drive Pattern
The 3-Drive pattern is similar to the AB=CD pattern, except that it has three legs and two retracements, whereas the AB=CD has two legs and one retracement. The 3-Drive pattern also resembles the Elliott Wave formation, which is one of the fundamental structures in technical analysis.
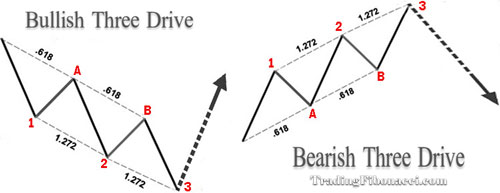 Basic Steps to identify the 3-Drive Pattern
Basic Steps to identify the 3-Drive Pattern
(1) Point A must be the 0.618 of Drive 1
(2) Point B must be the 0.618 retracement of Drive 2
(3) Drive 2 must be the 1.272 extension of correction A
(4) Drive 3 must be the 1.272 extension of correction B
(5) Ideally, the time required for the price to form Drive-2 equals the time for the formation of Drive-3
(3) The Gartley 222 Pattern
The Gartley 222 pattern was discovered by H.M. Gartley on page 222 of his book Profits in the Stock Market (1935).
The Gartley 222 incorporates the classic AB=CD formation with additional features. It is formed by five pivot or swing points, which can be visualized as follows:
-‘M’ for bullish patterns
-‘W’ for bearish patterns
The Gartley 222 Pattern Key Characteristics
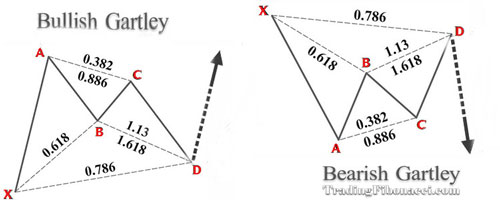 • The Point B must be the exact 61.8% retracement of XA
• The Point B must be the exact 61.8% retracement of XA
• The projection of BC must not exceed 1.618
• Point C point must be within the range of 0.382–0.886 retracement
• The point D must be precise 0.786 of the XA leg
• Ideally, AB must be equivalent to CD in length
• Ideally, the time required for the formation of AB equals the time required for the formation of CD
(4) The Bat Pattern
The Bat pattern is considered a highly reliable formation. One of its key advantages in trading is the ability to place a tight stop-loss. A tight stop-loss offers a favorable reward-to-risk ratio.
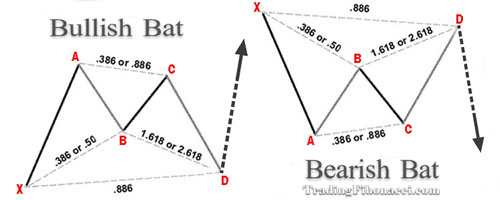 Bat Pattern Key Characteristics
Bat Pattern Key Characteristics
• The point B must be less than the 0.618 retracements of XA line, preferably the 50% or the 38.2% retracement of XA line
• The BC projection must be at least 1.618
• The point C ranges between 0.382 and 0.886
(5) The Crab Pattern
The Crab is a harmonic five-point formation. The pattern is confirmed upon completion when the XA leg projects to the 1.618 level.
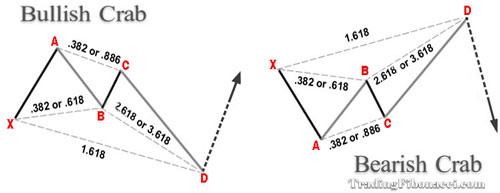 Crab Pattern Key Characteristics
Crab Pattern Key Characteristics
• Point B is the 0.618 or less retracement of XA line
• BC projection is 2.618 or 3.618
• XA projection at 1.618
• Point C ranges between 0.382 and 0.886
(6) The Butterfly Pattern
The Butterfly pattern, discovered by Bryce Gilmore, is another five-point harmonic formation.
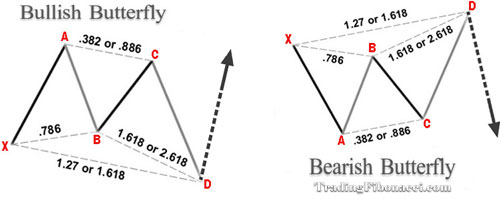 Ideal Butterfly Pattern Key Characteristics
Ideal Butterfly Pattern Key Characteristics
• Point B retraces 78.6% B of XA line
• The projection of BC must be 1.618, or more
• AB=CD must be met. There are alternatives but AB=CD is the most common
• Point C point must range between the 0.382–0.886 retracement
Basic Tips When Trading Using Harmonic Patterns
First, ensure your pattern calculations are accurate. Here are some additional tips:
-
Focus on Harmonic Patterns in Longer Timeframes
Avoid trying to spot harmonic patterns on short timeframes (M1, M5) as they are unreliable.
-
Pre-preparation
Create a list of trades approaching PRZ levels. PRZ stands for Potential Reversal Zone. Then, set automated alerts to monitor and trade them manually.
-
Use Pending Orders
If you cannot constantly monitor price action, use pending orders that activate when price meets specific criteria. Professional day traders often use pending orders.
-
Read the History of Price Action
History tends to repeat itself. Review past trades of the asset you plan to trade and study how price action confirmed reversals before.
-
Create a Trading Plan and Stick to It
Maintaining and following a trading plan with discipline is crucial. When market conditions become uncertain, your trading plan is your best protection.
W. D. Gann wrote in Truth of the Stock Tape (1923):
“Have a well-defined plan before you start trading, then follow that plan, as the architect does in building a house, or the engineer in constructing a bridge or driving a tunnel. The man who changes his ideas or his plan, which are based on something practical, for no other reason than that he hopes or fears the market will do something different, will never make a success.” More info: https://books.google.gr/books/about/Truth_of_the_Stock_Tape.html?id=v2dx0AEACAAJ&redir_esc=y
-
Don't Overtrade
The most important goal in trading is to stay alive. If you stay alive and have the skill, profits will come in the long run. Overtrading increases your overall market risk and can lead to losses over time.
Confirming Harmonic Price Reversals
After the price reverses from a harmonic area, the key factor in deciding whether to open a trade position is to evaluate the price action following the reversal. The following price action features can help traders confirm the reversal:
(1) Presence of a reversal candlestick pattern
(2) Increase in volume and volatility
(3) The faster the reversal occurs, the greater the potential for a strong move
(4) Confirmation of the reversal by MACD with standard settings (12, 26, 9) on the same timeframe (H1, H4, or D1)
Harmonic Patterns & Trading Setups
Harmonic patterns are highly profitable, with a success rate above 70%. The challenge is that these patterns are rare and difficult to identify, especially for non-professionals. Many plug-ins for MT4 and MT5 claim to automate this task. For traders wishing to spot and trade harmonic patterns, here are some basic questions that all valid setups should consider:
-
Does the price action indicate the presence of a potential pattern?
-
What type of pattern is it?
-
Is it a basic AB=CD pattern or another harmonic pattern?
-
Are there any other harmonic patterns in different timeframes that can confirm or negate this pattern?
-
Do time cycles confirm the existence of this pattern? (Time symmetry)
-
Where does the pattern complete?
-
At what price will the pattern become invalid? (Near this price, place your stop-loss order)
-
What is the optimal price for taking profits (take-profit order)?
-
What is the risk/reward ratio of this trade? (It should be above 2:1, preferably above 3:1)
-
How much of my capital should I risk on this trade? (Determining capital leverage)
■ Guide to Harmonic Trading and Harmonic Patterns
G.P. for TradingFibonacci.com (c)
Sources:
(i) TradingCenter.org
(ii) Harmonic Trading, Volume One {Scott M. Carney}
▶️ FIND OUT MORE AT TRADINGFIBONACCI.COM











